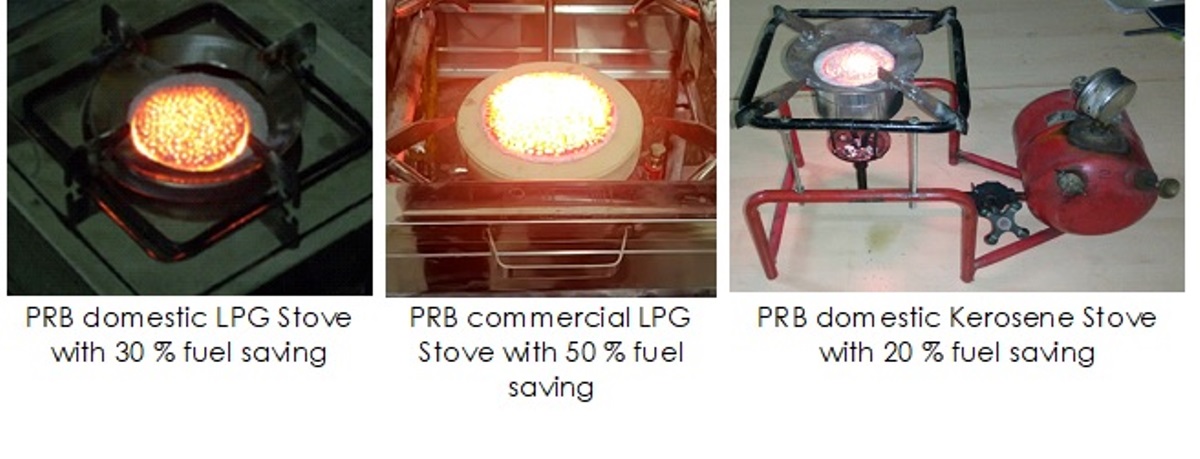
Developed by a Research Team headed by Prof. P. Muthukumar, the ‘Porous Radiant Burner’ provides fuel saving in the range of 25% to 50% and can be operated with LPG, Biogas and Kerosene
 KRC TIMES Education Desk
KRC TIMES Education Desk
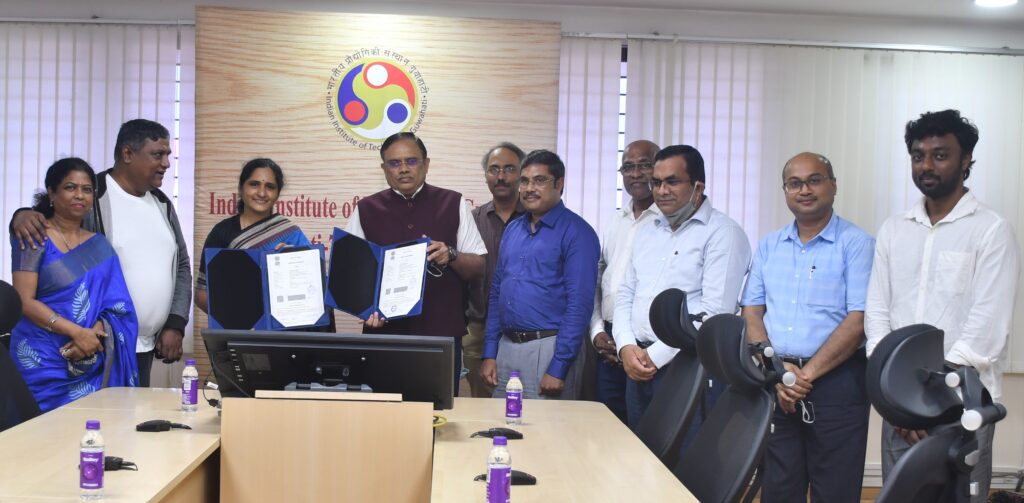
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati has transferred to an industry partner an energy-efficient and environment-friendly technology developed for cook-stoves by its researchers for commercialization. This will ensure that the benefits of the research reach society at large and benefit the common man.
A research team headed by Prof. P. Muthukumar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Guwahati, had developed ‘Porous Radiant Burners’ for cook-stoves equipped, which can provide the fuel-saving in the range of 25 to 50 percent. It can be operated with LPG, Biogas, and Kerosene.
This technology has been transferred to an industrial partner M/s. AGNISUMUKH ENERGY SOLUTIONS PRIVATE Ltd, Bangalore for commercialization. The MoU for this technology transfer was signed on 21st October 2021 in the presence of Prof. T. G. Sitharam, Director, IIT Guwahati, Faculty, Researchers, and other officials of IIT Guwahati and representatives from the Industry Partner.

This effort will be a major contribution of IIT Guwahati towards the Government of India’s efforts to enhance access to clean cooking energy by promoting LPG, biogas, and improved cook-stoves (ICS) through various policies and programs.
Highlighting the unique aspects of ‘Porous Radiant Burner,’ Prof. P. Muthukumar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Guwahati, said, “These indigenously developed cook-stoves equipped with specially-designed double layered PRBs provide fuel saving in the range of 25-50 % and reduces CO and NOx emissions by about 80 percent. The newly developed PRB is ideally suited both gaseous fuels like LPG, Biogas, PNG and liquid fuels like Kerosene, Methanol and Ethanol, for domestic as well as community/commercial cooking.”
The IIT Guwahati research team believes that the commercialisation of Porous Radiant Burner (PRB)-based LPG cookstoves across India will provide a huge LPG saving of about 13 lakh domestic cylinders per day and also will have a global impact on the burner-based applications.
Speaking on the occasion of MoU signing, Prof. T. G. Sitharam, Director, IIT Guwahati, said that-based cook-stove technology will play a key role in reducing the overall fuel consumption in the cooking sector, leading to a huge annual saving of about Rs. 50,000 crore for the Government, thus reducing the financial burden significantly and conserving energy. Further, it will also provide a better cooking environment by reducing CO and NOx emissions.
Industry partner, Mr Hari Rao, Chief Executive Officer, M/s. AGNISUMUKH ENERGY SOLUTIONS PRIVATE Ltd said, “Indian cooking system and global culinary world destroyed the nutrition of food by introducing modern fuel (LPG, Natural Gas) which reduced the intensity of heat but increased the pressure, while the traditional practice of cooking was based on intense heat totally on atmospheric pressure the Porous Radiant Burner technology will bring back the best practices in thermal management in cooking & industrial applications.”
One of the targets of Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7) is to ensure the availability and usage of clean cooking fuel to 100 percent of households by 2030. However, the SDG India dashboard indicates that only 56 percent of households use clean cooking fuel. The country needs to cover around 44 percent of households in the next nine years.
In order to achieve this goal, accessibility, affordability, and product awareness have to be considered while developing new sustainable cooking solutions. One of the important aspects of cooking solutions is the development of efficient and eco-friendly cook-stoves.
Being the second most populated country in the world, India has a large LPG consumer base (about 28 crores) which makes cooking an energy-intensive sector. Further, India imports about 50 percent of its LPG requirement. In this scenario, even a small improvement in the thermal efficiency of the cook-stove will result in a significant reduction in LPG imports for the Government.
Further, household pollution accounts for about 6.5 percent of the total deaths in India every year. Household air pollution is caused mainly by the use of polluting cooking fuels and inefficient cook-stoves. The use of PRB reduces CO and NOx emissions by about 80 percent, resulting in better indoor air quality.
Advertisements | 5E For Success

5 Advantages of KRC 5E MDP program, powered by KRC Foundation.
1. Employability training
2. Internship
3. Earn while you learn ( Work Experience Certificate, subject to selection and performance)
4. 100% Cashback on Fees through Global Garner
5. KRC Membership & Placement assistance.
Send your resume to get a free profiling session and selection.
Email resume: 5eforsuccess@gmail.com
WP: 9330830083





